Writing this article, we hope you’re in great health and won’t urgently need the vocabulary it covers. However, knowledge is power, and being prepared with useful hospital-related terms is wise. Today, we’ll explore the various departments and units that make up a typical hospital as well as the common equipment you might encounter. Whether you’re feeling fantastic or not, this vocabulary will undoubtedly prove useful, so let’s dive in.

Inside the Hospital
A hospital typically consists of several parts, departments, or stations that work together to provide comprehensive medical care. Here are some common components you would find in a hospital:
| Department | Definition | Additional details |
| Emergency Department/Room | The department where patients receive initial treatment for acute (1) illnesses or injuries. | Such acute illnesses may include severe respiratory distress (2), severe allergic reactions (3), acute stroke symptoms (4), etc. The examples of the injuries are trauma (5), fractures (6), burns and lacerations /ˌlæsəˈreɪʃnz/ (7). |
| Inpatient Units | The areas where patients stay overnight or longer for treatment and monitoring. They can include medical/surgical units, intensive care units, pediatric units, maternity units. | Medical/Surgical Units: general wards (8) for various medical conditions and surgeries. Intensive Care Units: specialized units for critically ill patients requiring intensive monitoring and treatment. Pediatric /ˌpiːdiˈætrɪk/ Units: units dedicated to the care of children. Maternity Units: areas for childbirth and postpartum /ˌpəʊst ˈpɑːrtəm/ (9) care. |
| Outpatient Clinics | The departments where patients receive treatment without being admitted, including primary care clinics, specialty clinics | Primary Care Clinics: general medical care and routine check-ups. Specialty Clinics: departments focused on specific medical specialties (e.g., cardiology (10), neurology (11), oncology (12)). |
| Diagnostic Services | The facilities for medical tests and imaging studies, such as radiology and laboratory | Radiology: X-rays, CT scans (13), MRIs (14), etc. Laboratory: blood tests, urine /ˈjʊrɪn/ tests, etc. |
| Operating Rooms | The surgical suites /swiːts/ where operations and procedures are performed | |
| Support Services | The services including pharmacy, nutrition services, physical therapy/rehabilitation /ˌriːəˌbɪlɪˈteɪʃn/ | Pharmacy: dispensing medications and pharmaceutical /ˌfɑːrməˈsuːtɪkl/ services. Nutrition Services: dietary /ˈdaɪəteri/ planning and food services. Physical Therapy/Rehabilitation: therapy for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. |
| Administrative and Support Departments | The departments handling admissions, medical records, billing and finance, human resources | Admissions: patient registration and paperwork. Medical Records: management of patient health records. Billing and Finance: handling of patient billing and insurance claims. Human Resources: management of hospital staff. |
| Ancillary /ˈænsəleri/ Services | The services including housekeeping, security and transportation |
- An acute illness or injury is very serious or severe. The opposite of an acute illness is a chronic illness.
- Respiratory distress is a condition where a person experiences difficulty breathing.
- An allergic /əˈlɜːrdʒɪk/ reaction occurs when the immune system overreacts to a substance that is normally harmless (allergen /ˈælərdʒən/).
- A stroke is a sudden serious illness when a blood vessel in the brain bursts or is blocked.
- A trauma /ˈtrɔːmə/ = an injury
- A fracture is a break in a bone.
- A laceration /ˌlæsəˈreɪʃn/ is a cut to the skin or body made with something sharp.
- A ward /wɔːrd/ is a separate room or area in a hospital for people with the same type of medical condition
- Postpartum (adj) refers to something connected with the period after the birth of a child: postpartum depression, period, care, check-up. The opposite of postpartum is antepartum /ˈæntiˈpɑːrtəm/.
- Cardiology /ˌkɑːrdiˈɑːlədʒi/ is the study and treatment of heart diseases. A doctor who specializes in cardiology is called a cardiologist /ˌkɑːrdiˈɑːlədʒɪst/.
- Neurology /nʊˈrɑːlədʒi/ is the scientific study of nerves and their diseases. A doctor who specializes in neurology is called a neurologist /nʊˈrɑːlədʒɪst/.
- Oncology /ɑːnˈkɑːlədʒi/ is the scientific study of and treatment of tumors in the body. A doctor who specializes in oncology is called an oncologist /ɑːnˈkɑːlədʒɪst/.
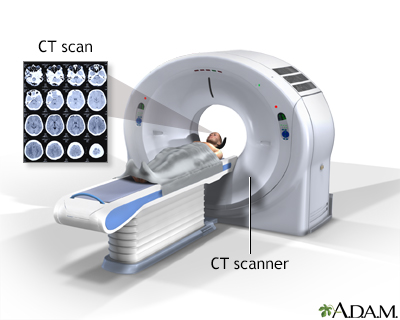
- A CT scan, or Computed Tomography scan, is a diagnostic medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
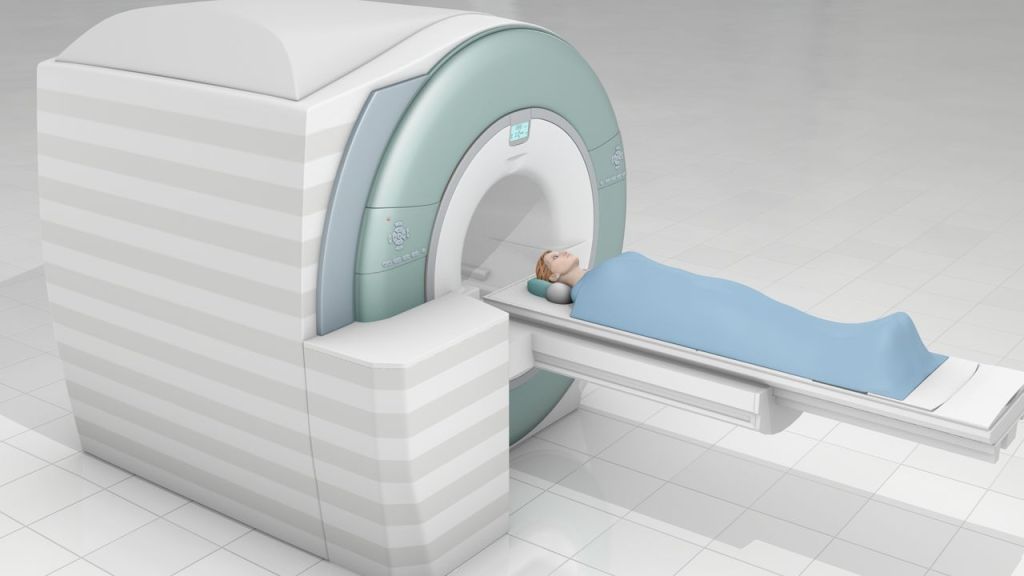
14. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a medical imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the organs and tissues inside the body.
15. Ancillary /ˈænsəleri/ services are essential support services that facilitate the main medical and administrative functions of the organization.
Practice 1
Exercise 1. Click the link here and match a hospital department with what it is responsible for.
Exercise 2. Click the link here and match the words with the pictures.
Exercise 3. Click the link here and choose the right words to complete the sentences.
Must-Know Medical Equipment
We’ve already introduced quite a bit of new vocabulary, but let us introduce 15 more items. If you feel you’ve absorbed enough for now and aren’t quite ready to engage with new vocabulary yet, revisit this article later when you’re refreshed and ready to expand your vocabulary further.
Practice 2
Exercise 4. Click the link here and match the words to their definitions.
Exercise 5. Click the link here and choose the right words to complete the sentences.
Did you enjoy the article? What new words learn? Would you like more content like this? Share your thoughts in the comments and subscribe to our blog for updates!